TM 9-2320-387-24-1
2-36. STARTER
CIRCUIT TESTS
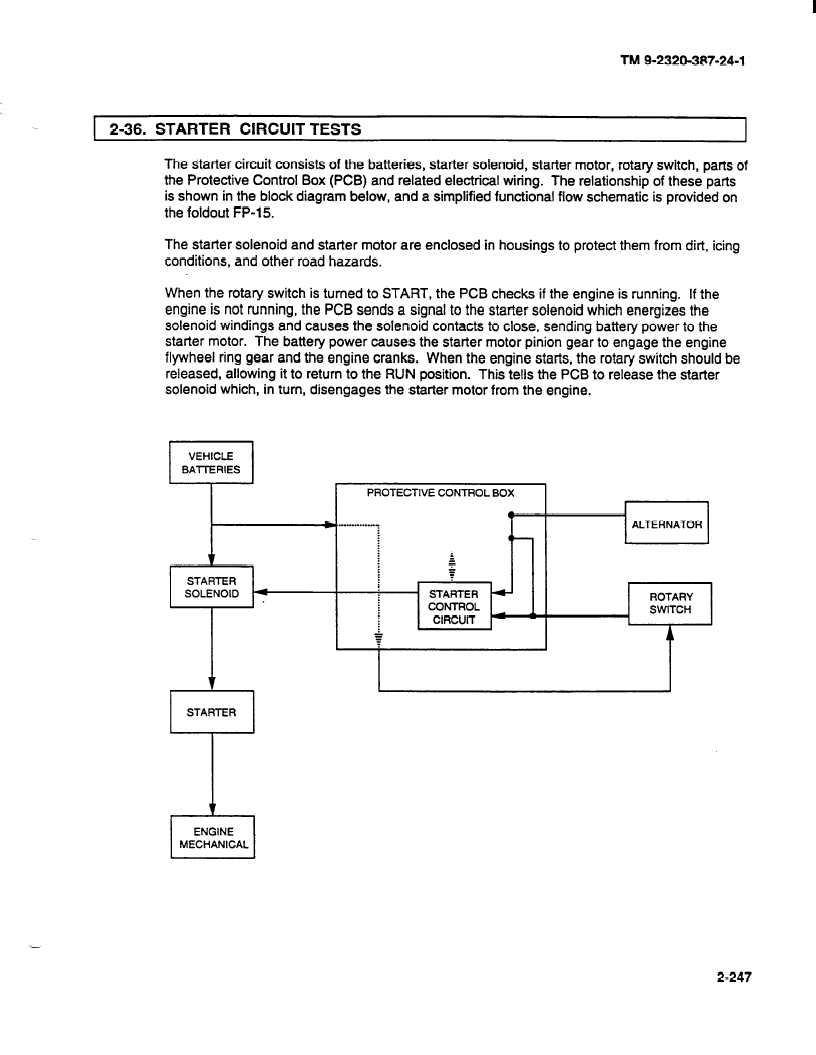
The starter circuit consists of the batteries, starter solenoid, starter motor, rotary switch, parts of
the Protective Control Box (PCB) and related electrical wiring. The relationship of these parts
is shown in the block diagram below, and a simplified functional flow schematic is provided on
the foldout FP-15.
The starter solenoid and starter motor are enclosed in housings to protect them from dirt, icing
conditions, and other road hazards.
When the rotary switch is turned to START, the PCB checks if the engine is running. If the
engine is not running, the PCB sends a signal to the starter solenoid which energizes the
solenoid windings and causes the solenoid contacts to close, sending battery power to the
starter motor. The battery power causes the starter motor pinion gear to engage the engine
flywheel ring gear and the engine cranks. When the engine starts, the rotary switch should be
released, allowing it to return to the RUN position. This tells the PCB to release the starter
solenoid which, in turn, disengages the starter motor from the engine.
PROTECTIVE CONTROL BOX
I
1
ALTERNATOR
+
A
<
z
STARTER
F
SOLENOID
-:
STARTER
4-
ROTARY
CONTROL
4
A
SWITCH
CIRCUIT
1
f
1,
4
STARTER
1
t
ENGINE
MECHANICAL
2-247